December 6, 2016
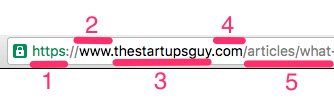
1. Protocol
It’s an agreement on how the server should communicate with your web browser. Few examples
- http: hyper text transfer protocol
- https: http with with SSL (encryption, secured)
- ftp: file transfer protocol
2. Subdomain
When you purchase a domain name, you can have “subdomains”, basically <anything>.yourdomain.com. They can be configured as separate websites or the same website – configurable to your liking.
Examples, if you purchased yourdomain.example.com you can have:
- andy.yourdomain.com
- jack.yourdomain.com
- hello.andy.yourdomain.com
- me.hello.andy.yourdomain.com
Interesting note: “www” is just a subdomain. Your website can be configured not to respond to www.yourdomain.com.
3. Top-level domain (TLD)
The domain name your purchased. Examples:
- yourdomain.com
- example.com
4. Extension
The extension of the domain name you purchased. Examples:
- .com
- .net
- .org
- .info
- .us
- .co
- .io
5. Path
Specific resource/file/page in the server you’d like to access.
Never miss new posts
Get the latest tech innovation news from Ryan delivered straight to your inbox!